Depth sounder numbers can be misleading due to environmental factors like surface turbulence, debris, or salinity changes, which distort signals. Device limitations and improper transducer placement also cause inaccurate results. Regular calibration and proper maintenance help keep readings reliable. External interference or water conditions often skew data, making it seem inconsistent or false. To navigate safely, understanding these factors will help interpret the numbers correctly—keep reading to discover how to spot and fix common issues.
Key Takeaways
- Environmental factors like surface turbulence, debris, or temperature shifts can cause sonar signals to distort, leading to inaccurate depth readings.
- Proper transducer placement and maintenance reduce interference from turbulence, bubbles, or fouling, improving measurement reliability.
- Signal processing limitations and water properties, such as salinity and temperature, affect sound speed, causing potential discrepancies in depth data.
- Regular calibration and inspection help detect sensor drift or damage that may cause false or inconsistent readings.
- Cross-verifying depth readings with known benchmarks or different methods can help interpret and correct misleading sonar numbers.

Estink Depth Sounder Kit, DC 12V IP67 Dash Depth Finder Transducer with White Backlight Digital Boat Depth Finder Marine Instruments for Yachts Fishing Boats Marine Transportation
INSTANT DEPTH INDICATION: With a working voltage of 9-32V and up to 16V, our dash depth sounder device…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
How Do Depth Sounders Measure Underwater Terrain?
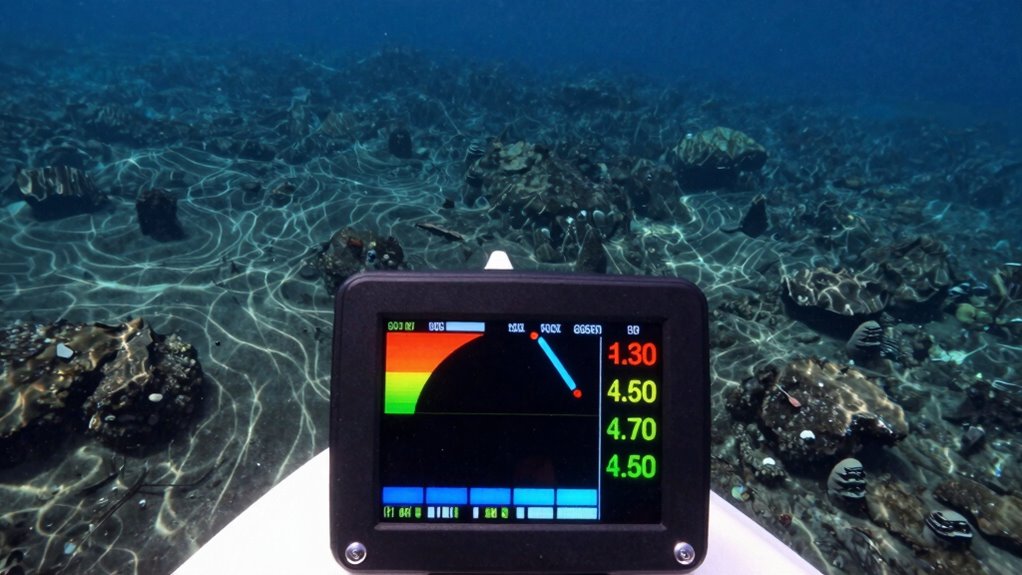
Depth sounders measure underwater terrain by emitting sonar waves that travel through the water and bounce off the seafloor. The sonar frequency you choose affects how well the device penetrates the water column and details the seabed. Higher frequencies provide more detailed images but don’t travel as far, making them ideal for shallow waters. Lower frequencies penetrate deeper into the water column, allowing you to detect structures or fish schools farther from the boat. When the sonar wave hits the seafloor, it reflects back to the transducer, which calculates depth based on the time it takes for the echo to return. Understanding how sonar frequency interacts with the water column helps you interpret depth readings accurately and avoid misleading data caused by factors like water conditions or target size. Exploring digital signal processing can further enhance your understanding of sonar technology and its limitations.

Ahuliao Boat Transducer Mounting Plate Transom Saver Mount Board Stern Saver Mounting Block Marine Transducer Mounting Bracket for Fish Finder & Sonar 12" X 3.5" X 0.75" – White
【Transom Mounting Plate Adaptability】Transom mounting plate is designed for all types of boats and is very suitable for…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Common Causes of Deceptive Depth Readings

Salty water can cause your depth readings to become inaccurate by increasing sound wave absorption. Improper transducer placement also leads to false readings or noisy displays. Understanding these common issues helps you identify and correct potential problems quickly. Additionally, proper maintenance of your equipment can prevent many common inaccuracies.
Salty Water Effects
When your depth sounder shows inconsistent or unusually shallow readings in salty water, the high salinity levels are often to blame. Salty water affects sound wave propagation by increasing the speed at which sound travels through it. This change can cause the sound waves to reflect or refract differently, leading to inaccurate depth readings. Because salt ions alter the water’s density and sound velocity, your device may interpret these signals as shallower depths than actual. It’s essential to recognize that the increased salinity can distort the sound pulses, making it tricky to get precise measurements. To mitigate this, consider calibrating your depth sounder for salty conditions or applying correction factors to improve accuracy in high-salinity environments. Additionally, understanding how sound wave propagation is affected by salinity can help you interpret readings more effectively. Recognizing the impact of salinity levels on sound velocity is crucial for accurate measurements in varying water conditions. Furthermore, using proper calibration techniques tailored for salty environments can significantly enhance measurement reliability. Being aware of how salinity variations influence sound travel can also assist in troubleshooting inconsistent readings.
Transducer Placement Issues
Incorrect transducer placement is a common cause of deceptive depth readings. If your transducer isn’t positioned properly, the sonar beam may not point straight down, affecting accuracy. A misaligned transducer angle can cause the sonar beam to skim the bottom instead of hitting it directly, resulting in readings that are shallower or deeper than reality. Placing the transducer too high or at an improper angle can create false echoes or reflect signals away from the bottom. Make certain the transducer is mounted flat and at the correct angle for your boat’s hull. Regularly check the mounting position and angle to prevent these issues. Proper placement guarantees the sonar beam penetrates straight downward, providing reliable depth readings you can trust. Additionally, cable failures or interference can also lead to inaccurate readings, so inspecting and maintaining your wiring is essential. Ensuring your transducer is free of electrical interference helps maintain accurate depth readings. Furthermore, regular maintenance of your sonar equipment can help identify potential issues before they cause inaccurate readings.

JOYWEE FF688C 3.5" Phiradar Color LCD Boat Fish Finder 200KHz/83KHz Dual Sonar Frequency 80M 240ft Detection Muti-language Auto zoom
This amazing fish finder is specially designed for amateur and professional fishermen to find fish location, depth and…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
How Water Conditions Affect Depth Accuracy
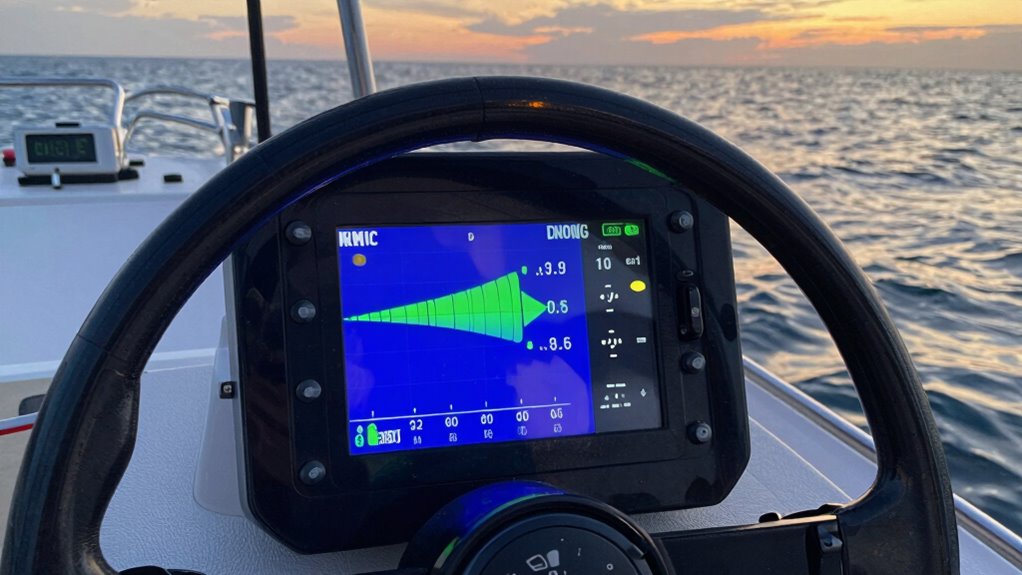
Water conditions can considerably influence the accuracy of depth sounder readings. Poor water clarity, such as murky or algae-filled water, causes the sound waves to scatter, resulting in unreliable depth measurements. When visibility is low, the transducer may pick up false echoes or struggle to distinguish the bottom from suspended particles. Temperature effects also play a role; warmer water can change sound speed, leading to slight inaccuracies if your device doesn’t adjust for temperature variations. Sudden temperature shifts or thermoclines can cause the sound waves to refract or bend, distorting depth readings. Being aware of these conditions helps you interpret your sounder data more accurately, recognizing when environmental factors might be skewing the numbers and avoiding misjudged depths. Additionally, understanding water properties can help you better anticipate how external factors influence your readings. Recognizing sound wave behavior in different water conditions can further improve your interpretation skills, especially when considering sound wave interactions with various substances in the water. Knowing how water chemistry affects sound transmission can also aid in more precise depth assessments. In addition, fluctuations in water salinity can impact the speed of sound and thus your depth calculations.

Venterior Portable Rechargeable Fish Finder Wireless Sonar Sensor Fishfinder Depth Locator with Fish Size, Temperature, Bottom Contour, Color Display
Castable: No more long & heavy cable for transducer. Clear Color Screen: it comes with clear color TFT…
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
As an affiliate, we earn on qualifying purchases.
Proper Transducer Placement for Reliable Readings

To get accurate depth readings, you need to position your transducer correctly. Make certain it’s mounted at the ideal angle and depth for your boat’s setup. Also, keep it away from sources of signal interference like hull turbulence or electrical noise to guarantee reliable results. Proper placement ensures that the transducer’s signal transmission is not hindered by external factors, leading to more consistent readings. Additionally, integrating connected fitness technology can help monitor and optimize your boat’s equipment setup, ensuring it remains in the best condition for accurate readings. Regularly checking transducer alignment and maintaining a clean surface further contribute to reliable depth measurements.
Optimal Transducer Positioning
Proper transducer placement is essential for obtaining accurate depth readings, as even small changes in position can considerably impact the results. To guarantee reliable data, focus on optimizing transducer tilt and mounting height. Keep the transducer level; excessive tilt causes signal distortion and inaccurate readings. Adjust the mounting height so the transducer is submerged enough to avoid air bubbles and surface interference but not so deep that it loses sensitivity. The ideal positioning minimizes turbulence and maintains a steady, clear signal. Always test different placements to identify the position that provides the most consistent and accurate readings. Properly aligning and securing the transducer ensures consistent data, helping you interpret depths correctly without being misled by false or fluctuating numbers. Calibration techniques can further enhance measurement accuracy and reliability. Additionally, monitoring for environmental factors such as surface conditions or nearby objects can help maintain measurement integrity. Being aware of device limitations is also crucial, as no transducer can provide perfect data in every condition.
Minimize Signal Interference
Minimizing signal interference starts with carefully positioning your transducer to avoid sources of disturbance. Place it away from electronic devices, motors, or wiring that generate noise, which can distort readings. Ensure the transducer is mounted securely and at an ideal angle to reduce turbulence and bubble formation. Use noise reduction techniques, such as adjusting the transducer’s frequency or sensitivity settings, to filter out unwanted signals. Additionally, applying electronic shielding around the transducer’s cables helps prevent electromagnetic interference from external sources. Proper shielding minimizes signal noise, resulting in more accurate depth readings. Regularly inspect and maintain your setup to keep interference levels low. Proper transducer placement** is vital for achieving clearer signals and more reliable depth sounder performance. By paying close attention to placement and shielding, you’ll achieve clearer signals and more reliable depth readings. Considering the impact of zodiac traits and personalities can also help you understand how external factors might influence your setup and interpretation of data. Furthermore, understanding the best settings** for your device can significantly improve measurement accuracy and reduce misleading readings.
Why Regular Calibration Keeps Your Depth Readings Accurate

Regular calibration is essential to make certain your depth sounder provides accurate readings every time you’re on the water. Over time, sensor drift can cause your device to become less precise, leading to misleading depth measurements. Regular calibration helps counteract this drift, ensuring your depth readings stay reliable. How often you calibrate depends on your usage and water conditions, but a good rule of thumb is to check and recalibrate periodically—especially after rough weather or heavy use. Consistent calibration maintains the sensor’s accuracy, preventing small errors from compounding into bigger problems. By staying on top of calibration frequency, you ensure your depth sounder continues to give trustworthy data, helping you navigate safely and make better decisions on the water.
Troubleshooting Inconsistent Depths

When your depth readings become inconsistent, it can be frustrating and potentially dangerous. To troubleshoot, start by checking your sensor calibration; an uncalibrated sensor can cause erratic data. Next, consider water salinity, as changes in salinity affect sound speed, leading to inaccurate depths. Finally, inspect for any debris or buildup on the sensor that could interfere with signals. Remember:
- Regularly recalibrate your sensor to guarantee accuracy.
- Adjust for water salinity variations, especially in changing conditions.
- Keep the sensor clean to prevent signal interference.
Sources of Signal Interference That Skew Depth Data

Signal interference from external sources can markedly distort depth sounder readings, making it essential to identify and mitigate these disruptions. Electronic interference from nearby equipment, such as radios or power lines, can create false signals, leading your depth readings astray. Vessel vibrations caused by engine operations or rough seas also interfere, shaking the transducer and skewing data. Visualize these influences with this table:
| Interference Source | Effect on Depth Data | How to Minimize |
|---|---|---|
| Electronic Devices | False echoes, noise | Keep devices away from transducer |
| Engine Vibrations | Erratic depth readings | Reduce engine load or isolate transducer |
| External Signals | Signal distortion | Use shielding or filters |
Recognizing these factors helps you interpret depth data accurately, avoiding misleading numbers.
Best Tools and Techniques to Cross-Check Water Depth

To guarantee the accuracy of water depth readings, you should use a combination of reliable tools and techniques to cross-check data. First, regularly perform sonar calibration to ensure your device is providing accurate measurements. Second, account for water salinity, as it affects sound speed and depth calculations—adjust your transducer settings accordingly. Third, compare your sonar readings with known depth markers, such as charts or physical measurements, to verify accuracy. Additionally, monitor water salinity levels and recalibrate when conditions change. Using these methods helps identify discrepancies caused by salinity shifts or equipment drift. Ultimately, combining proper calibration, awareness of salinity impacts, and validation against physical markers guarantees trustworthy depth data.
When to Consider Replacing Your Transducer?

A transducer is a critical component of your depth sounder, and recognizing when it needs replacing can prevent inaccurate readings and potential equipment failure. Typically, transducers have a lifespan of about 3 to 5 years, depending on usage and water conditions. Replacement indicators include persistent false readings, inconsistent depth signals, or a gradual decline in accuracy despite cleaning and calibration. If your depth sounder shows erratic behavior or if the transducer surface becomes damaged or fouled beyond cleaning, it’s time to think about a replacement. Ignoring these signs can lead to unreliable data, risking navigation safety. Regularly inspect your transducer and heed these replacement indicators to ensure your depth sounder remains dependable when you need it most.
Final Tips to Trust and Verify Your Depth Sounder Readings

To guarantee your depth sounder readings are accurate, you should regularly cross-check them with navigation charts and local data. Calibrating your equipment often helps maintain reliability, especially in changing conditions. Understanding the signal limitations of your device prevents misinterpretations and keeps your readings trustworthy.
Cross-Check With Charts
While your depth sounder provides valuable readings, it’s essential to cross-check those numbers with existing charts. This helps verify accuracy and catch discrepancies caused by sonar calibration issues or interference. Use a chart overlay to compare sounder data directly with reliable chart depths. To guarantee trustworthy readings, consider these tips:
- Confirm the sonar calibration is accurate before navigation.
- Overlay your depth sounder data onto charts to identify inconsistencies.
- Cross-reference known underwater features to validate your readings.
This process helps you spot errors and build confidence in your data. Remember, charts are based on surveyed data and can reveal if your sounder is giving false readings. Trust but verify—your safety depends on it.
Regularly Calibrate Equipment
Regularly calibrating your depth sounder is crucial to guarantee accurate readings and safe navigation. Proper sensor maintenance keeps your equipment in top condition, preventing drift and inaccuracies. Use calibration techniques like testing in shallow, known depths to verify readings, and adjust settings as needed. Keep sensors clean and free of debris, algae, or corrosion that can distort signals. Regular checks ensure the device responds correctly to changes in water depth and maintains precision over time. If your depth sounder isn’t calibrated properly, you risk misjudging water depths, which can lead to accidents. Incorporate routine calibration into your maintenance schedule, and don’t skip sensor inspections. Trustworthy readings depend on consistent sensor care, proper calibration techniques, and vigilant maintenance. Accurate data keeps your navigation precise and safe.
Understand Signal Limitations
Even with proper calibration and maintenance, understanding your depth sounder’s signal limitations helps guarantee you can trust its readings. Signal processing and transducer technology can be affected by environmental factors, causing inaccuracies. To improve reliability:
- Recognize that poor signal processing can cause echoes to be misinterpreted, leading to false readings.
- Understand that transducer technology may struggle with certain bottom types or depths, reducing accuracy.
- Be aware that surface conditions like waves or debris can distort the signal, making it harder to interpret real depth.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Depth Sounders Detect Underwater Objects Besides the Bottom?
Yes, your depth sounder can detect underwater obstacles and even fish. It sends out sonar waves that bounce off objects beneath the surface, revealing underwater obstacles and schools of fish. However, interpreting these signals requires understanding that not everything detected is the bottom; some signals may be false echoes or debris. So, stay alert to differentiate between the actual seabed and other underwater features or fish.
How Does Salinity Influence Depth Measurement Accuracy?
Salinity effects water density, which directly impacts depth measurement accuracy. Higher salinity increases water density, causing sound waves to travel faster and potentially leading to shallower readings. Conversely, lower salinity decreases density, slowing sound waves and making depths appear deeper than they are. To guarantee precise measurements, consider salinity effects and calibrate your depth sounder accordingly, especially when operating in areas with varying salinity levels.
Are There Specific Water Conditions That Cause the Most Errors?
Imagine trying to see through foggy glass—that’s what murky water does to your depth readings. Water clarity drops, and temperature fluctuations cause sound waves to bend unpredictably, leading to errors. Turbid or thermally unstable conditions distort the sound signals, making your depth measurements less reliable. When water’s murky or temperature shifts rapidly, you can bet your depth sounder will give you a misleading picture, so stay alert.
What Are Signs My Depth Sounder Needs Professional Maintenance?
You’ll need professional maintenance if your depth sounder shows inconsistent readings or suddenly jumps, which could signal sensor calibration issues. Also, watch for power supply problems, like degraded batteries or loose connections, causing erratic performance. Regularly inspect and test your device; if problems persist despite basic troubleshooting, it’s time to get expert help to guarantee accurate depth readings and reliable operation.
Can Software Updates Improve Depth Reading Reliability?
Like a trusty steamboat steering tricky waters, software updates can improve your depth reading reliability. They often include firmware enhancements that address calibration challenges, making measurements more accurate. Regular updates ensure your depth sounder adapts to changing conditions and corrects errors. Don’t ignore these updates—think of them as essential repairs to keep your device running smoothly, giving you confident readings and safer trips on the water.
Conclusion
Remember, depth sounders aren’t foolproof—they can deceive you if you don’t understand their quirks. Water conditions, transducer placement, and signal interference all play a role in skewed readings. Trust your instincts and cross-check with other tools. Regular calibration and maintenance are key. Don’t fall for the myth that a single reading is always accurate—stay vigilant, question the numbers, and you’ll navigate safely and confidently through any underwater terrain.